time:Dec 28, 2024 source:ZEXCIT
Selecting the appropriate vibrating screen exciter is crucial for the efficient operation of a vibrating screen, as it directly affects the screen’s performance, including vibration intensity, frequency, and amplitude. The exciter generates the required vibration to separate materials on the screen. Below is a step-by-step guide to selecting the right exciter for your vibrating screen.
Before choosing an exciter, it's essential to understand the specific requirements of your vibrating screen:
Screen Type: Determine the type of screen you are using (e.g., linear, circular, elliptical, etc.).
Vibration Motion: Define the desired vibration motion (e.g., linear, circular) and amplitude.
Load and Throughput: Determine the expected load on the screen and the desired material throughput.
Screen Size: Identify the dimensions of the vibrating screen, including width, length, and deck number.
Material Characteristics: Consider the properties of the material being processed (e.g., dry, wet, sticky, large lumps).
Exciters come in different types based on the mechanism used to create vibration. The most common types are:
A. Electric Exciter
Principle: Uses an electric motor with an unbalanced weight to generate vibration.
Use Case: Commonly used in linear or circular vibrating screens.
Advantages:
Simple, cost-effective, and reliable.
Easy to adjust vibration frequency.
Disadvantages:
Limited power output compared to hydraulic exciters.
Can require maintenance due to motor wear.
B. Hydraulic Exciter
Principle: Uses hydraulic pressure to generate motion and vibration.
Use Case: Suitable for heavy-duty applications and larger screens.
Advantages:
Can generate higher power and is ideal for applications involving large screens and heavy loads.
Adjustable amplitude and frequency.
Disadvantages:
More complex and expensive than electric exciters.
Requires a hydraulic system for operation.
The exciter's vibration characteristics (frequency, amplitude, and direction) should match the operational requirements of the vibrating screen:
Frequency:
The frequency (usually expressed in revolutions per minute, RPM) determines how fast the screen vibrates.
A higher frequency can increase screening efficiency for fine materials.
Amplitude:
Amplitude controls the intensity of vibration and the ability to move large particles.
Larger amplitudes are better for heavier materials and larger particles.
Direction of Vibration:
Make sure the exciter can produce the correct directional motion (horizontal, vertical, or elliptical) depending on your screen type.

Exciter Force: The exciter must generate a sufficient force to overcome the mass of the material on the screen and achieve effective separation.
Power:
The exciter must provide enough power for the screen to operate at the required capacity and efficiency.
The exciter power (in kW or HP) depends on the screen size, material characteristics, and desired performance.
Exciter Force Calculation:
The exciter force can be calculated using the formula:where F is the force in Newtons, m is the mass of the material (kg), and a is the acceleration (m/s²) induced by the vibration.
For Smaller Screens: Electric exciters with lower power outputs are generally sufficient for smaller screens with lighter loads.
For Larger Screens: Hydraulic exciters or larger electric exciters may be needed for larger screens or heavy-duty applications.
For Heavy or Sticky Materials: Larger exciters (hydraulic or high-power electric) are typically needed to move larger or sticky materials.
Adjustability:
Some exciters offer adjustable amplitude and frequency, which can be beneficial in fine-tuning the screening process.
Check if the exciter allows you to adjust parameters according to varying material characteristics.
Maintenance:
Electric exciters are generally easier to maintain due to fewer moving parts compared to hydraulic exciters.
Hydraulic exciters require a reliable hydraulic system and regular maintenance.
Ensure that the exciter is compatible with your existing vibrating screen in terms of mounting, vibration type, and power requirements:
Mounting Type: Verify that the exciter can be easily mounted to your screen, considering the design and structure.
Vibration Direction: Ensure the exciter produces the required vibration direction (e.g., linear, circular, elliptical) to match the screen's design.
Quality and Reliability: Choose an exciter from a reputable manufacturer known for producing reliable and high-quality equipment.
Support and Service: Ensure the manufacturer provides good after-sales support, including technical assistance, spares, and servicing.
Initial Cost: The cost of the exciter depends on the type (electric vs. hydraulic) and the size/power required.
Operational Costs: Electric exciters tend to have lower operational costs compared to hydraulic ones due to energy efficiency and lower maintenance.
Long-Term Reliability: Consider the long-term costs of maintenance, durability, and efficiency when selecting the exciter.
Conclusion
To select the right vibrating screen exciter, consider the screen type, vibration characteristics, material properties, power requirements, and budget. By ensuring compatibility with the operational needs and screen specifications, you can improve the efficiency, performance, and longevity of your vibrating screen.
What is the price of a vibrating feeder and what are the factors that affect its price?
What is the role of vibrating screen exciter

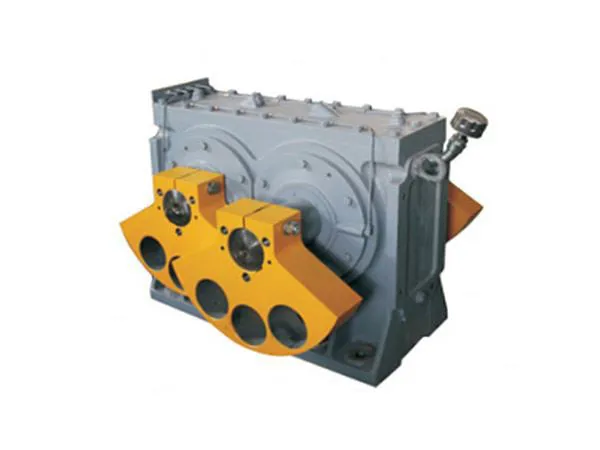
The DF Series Vibrator refers to a range of specialized vibrators used in various industrial applications to generate controlled vibrations. These vibrators are designed for reliability, durability, and efficiency, making them suitable for integration into equipment such as vibrating screens, feeders, conveyors, compactors, and sieves.
READ MORE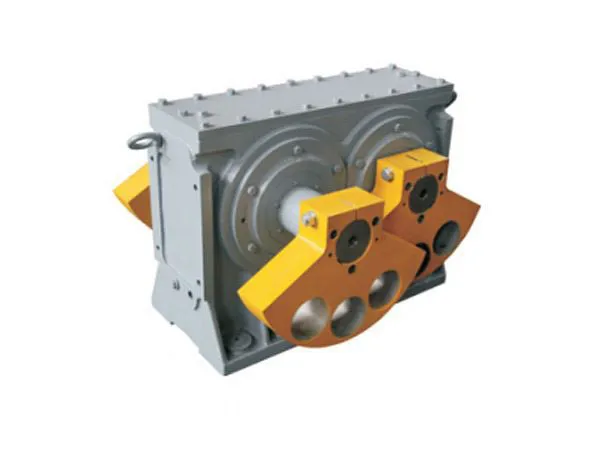
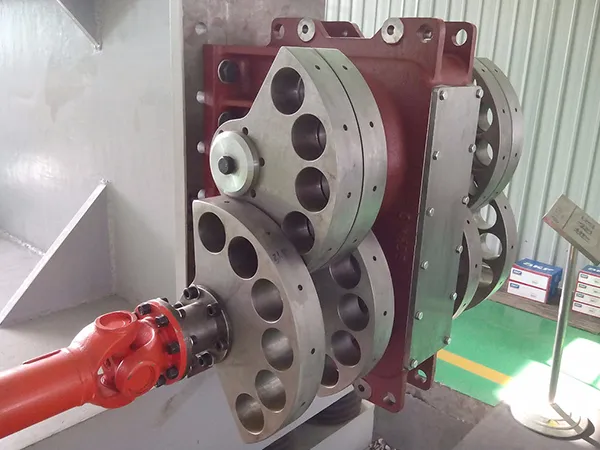
NE Series Vibrators are versatile and reliable components used in a wide range of industrial applications to generate controlled vibrations for material handling, processing, compaction, and testing purposes. Their robust construction, high efficiency, and adjustable settings make them suitable for various industries requiring vibration-based solutions.
READ MORE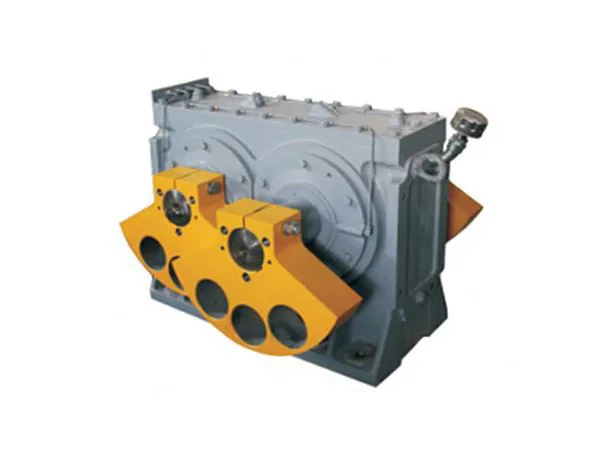
The FE series vibrator is a specialized component used in various industrial applications to generate controlled vibrations. These vibrators are designed to be reliable, durable, and efficient, making them suitable for integration into equipment such as vibrating screens, feeders, conveyors, compactors, and sieves
READ MORECopyright © 2023 Xinxiang Zongyuan Machinery Equipment Co., Ltd. | All Rights Reserved.