time:Apr 07, 2025 source:ZEXCIT
Vibrating screens play a vital role in many industries, including mining, construction, metallurgy, and recycling. These machines ensure efficient material separation and improve productivity. However, like any heavy-duty equipment, vibrating screens require regular maintenance to operate at peak performance and avoid unexpected breakdowns. Proper maintenance not only extends the machine's lifespan but also ensures safety and minimizes downtime. In this guide, we’ll share practical vibrating screen maintenance tips to help you keep your equipment running smoothly and efficiently.Maintaining vibrating screens effectively is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, maximizing lifespan, and preventing costly downtime.
Listen for Abnormal Noises: Pay attention to any unusual grinding, knocking, rattling, or high-pitched sounds coming from the bearings, motor, or structure.
Observe Vibration: Check for smooth, consistent vibration across the entire screen deck. Look for erratic movement, shaking, or excessive bouncing, which could indicate imbalance, broken springs, or structural issues.
Check Material Flow: Ensure material is feeding evenly onto the screen and discharging properly. Look for build-up on side plates, feed boxes, or discharge lips.
Check for blinding (screen openings clogged) or pegging (near-size particles stuck).
Visual Scan for Obvious Damage: Quickly look for loose bolts, cracked welds (especially near high-stress areas), obvious holes or tears in the screen media, and damaged spray nozzles (if applicable).
Check Surrounding Area: Look for excessive spillage or dust, which might indicate worn seals or enclosure issues. Ensure walkways and access points are clear.
Screen Media Inspection (Crucial!):
Tension: Ensure screen panels (especially wire mesh) are properly tensioned. Loose screens wear out quickly, perform poorly, and can damage the screen box.
Check tensioning bolts/clamps.
Wear & Damage: Inspect for broken wires, tears, holes, excessive wear, or deformation in wire mesh, polyurethane, or rubber panels. Note wear patterns – uneven wear might indicate feed issues.
Blinding/Pegging: Check closely for clogged openings. If persistent, investigate the cause (moisture, particle shape, wrong opening size).
Clamping System: Inspect clamp bars, J-bolts, wedges, and associated hardware for wear, damage, or looseness. Ensure they are securing the media effectively.
Vibrator / Exciter Mechanism:
Bearing Temperature: Safely check bearing housing temperatures (using an IR temp gun is ideal). Compare readings over time and between bearings. A significant increase indicates potential problems.
Lubrication Levels (Oil): Check sight glasses for correct oil levels. Look for leaks around seals.
Grease Points: Check for signs of fresh grease purging (if grease lubricated) indicating proper lubrication. Clean excess old grease.
Mounting Bolts: Verify that the bolts securing the vibrator mechanism to the screen box are tight.
Drive System:
V-Belts: Check tension (not too tight, not too loose), wear (cracks, glazing), and alignment. Misaligned belts wear quickly and waste energy.
Drive Motor: Listen for bearing noise. Check mounting bolts. Ensure cooling fins are relatively clean.
Guards: Ensure all drive guards are securely in place.
Support Structure & Springs:
Springs (Coil or Rubber): Inspect for cracks, breakage, sagging, or deformation. Ensure the screen is sitting level.
Support Structure: Perform a more thorough check for cracks in welds or structural members, especially around spring mounts and support points. Check mounting bolts securing the screen to the structure.
Fasteners: Check the tightness of key bolts, particularly those holding the screen media, vibrator mechanism, side plates, and support structure connections. Use torque wrenches where specified.
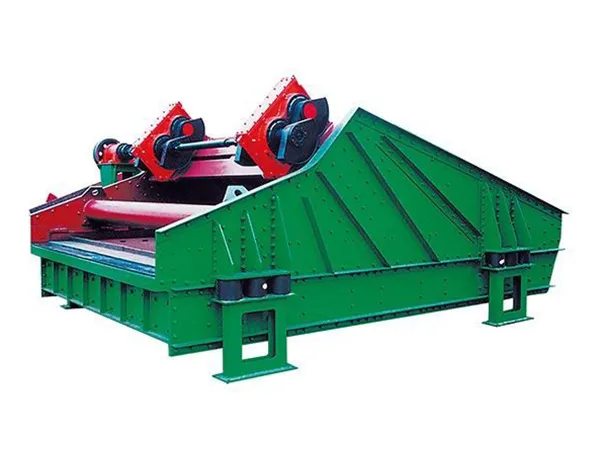

Lubrication (Vital!):
Follow the Manual: Adhere strictly to the manufacturer's specifications for lubricant type (oil or grease), quantity, and frequency.
Greasing: Use the correct grease type. Do not over-grease bearings, as this can cause overheating. Purge old grease if recommended.
Oil Changes: Change oil at recommended intervals. Check for contaminants (water, metal particles) in the old oil.
Thorough Structural Inspection: Clean high-stress areas and inspect carefully for fatigue cracks, especially around welds connecting side plates, cross members, and vibrator mounts.
Component Replacement: Replace worn components proactively based on inspection findings or expected lifespan (e.g., screen media, springs, bearings, belts).
Alignment Checks: Periodically verify motor-to-exciter alignment.
Cleaning: Thoroughly clean built-up material from the screen box and structure, as this can cause imbalance and hide potential problems.

Safety First: ALWAYS follow Lockout/Tagout procedures before performing any maintenance. Ensure the screen has come to a complete stop and cannot be accidentally started.
Read the Manual: The manufacturer's operation and maintenance manual is your primary resource. Follow its specific recommendations.
Keep Records: Maintain a logbook of inspections, maintenance performed, parts replaced, and any issues found. This helps track trends and schedule future work.
Use Quality Parts: Use OEM or high-quality equivalent replacement parts, especially for critical components like bearings and screen media.
Operator Training: Ensure operators are trained to recognize warning signs (noises, vibrations) and report them promptly.
Maintain Proper Feed: Ensure the feed rate and presentation to the screen are consistent and within design limits. Overloading stresses the screen and reduces efficiency.
By implementing a consistent maintenance program incorporating these tips, you can significantly improve the reliability, efficiency, and service life of your vibrating screens.
How to reduce noise in vibrating screen operation
No information
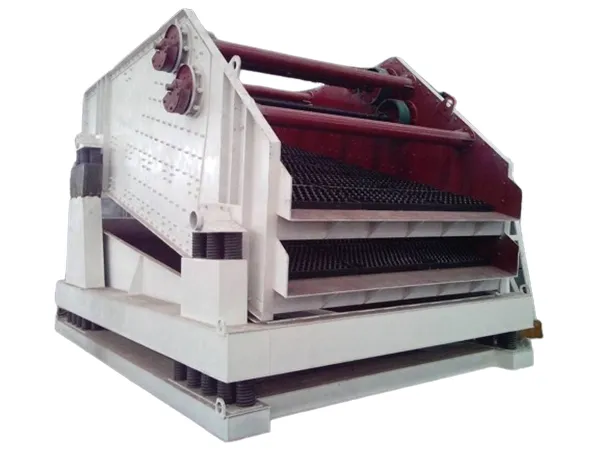

ZSK eccentrics series linear vibrating screen is a new and efficient universal screening equipment, screen box trajectory which is approximately a straight line. This series of screen machine embodies most of the advantages of a biaxial linear screen, with the most extensive scope and application prospects.
READ MORE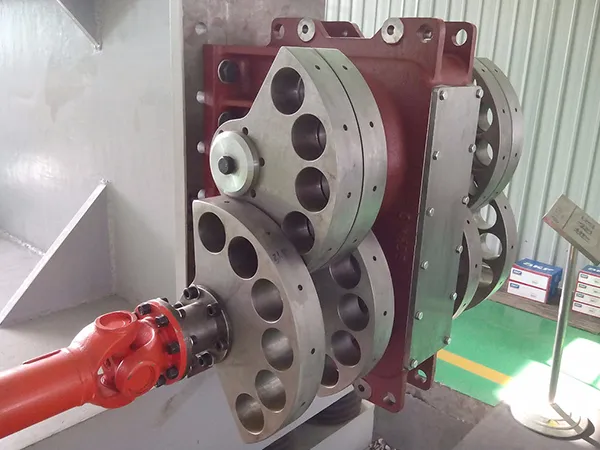
The DF Series Vibrator refers to a range of specialized vibrators used in various industrial applications to generate controlled vibrations. These vibrators are designed for reliability, durability, and efficiency, making them suitable for integration into equipment such as vibrating screens, feeders, conveyors, compactors, and sieves.
READ MORE
A flip flop vibrating screen is a type of vibrating screen that utilizes the principle of elasticity to effectively screen and separate fine materials. This unique design creates a flip-flop motion during the screening process, which helps prevent material blinding and pegging.
READ MORECopyright © 2023 Xinxiang Zongyuan Machinery Equipment Co., Ltd. | All Rights Reserved.